en
+
Electric power systems are one of the cornerstones of modern society, supporting the normal operation of industry, commerce, households, and various facilities. It is not only a critical network for energy transmission but also an indispensable part of economic development and daily life. The power system consists of multiple stages such as power generation, transmission, and distribution, among which the distribution network and its secondary system play a crucial role. The distribution network is the last link in the power system, directly distributing electricity to users and ensuring smooth transmission of electricity from the power generation end to the usage end.
Composition of the Power System
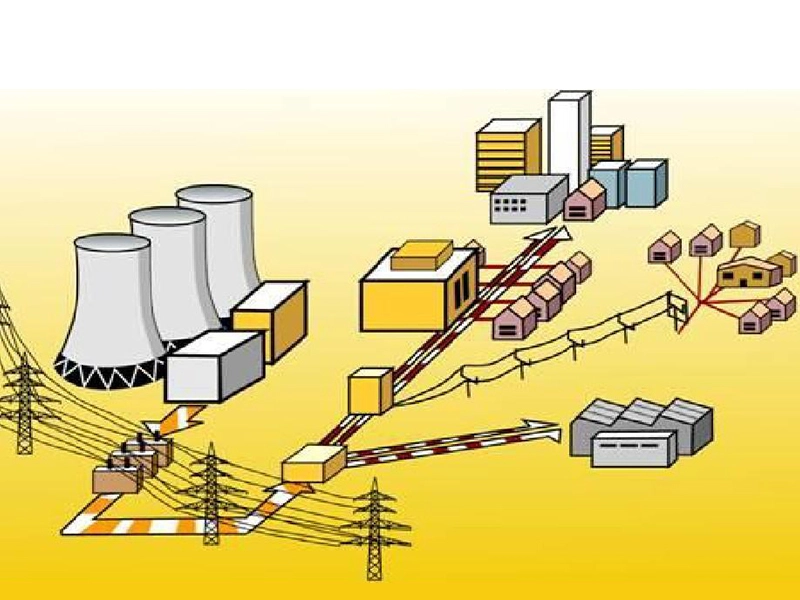
The basic composition of the power system includes three main parts: power generation, transmission, and distribution. Each part assumes specific responsibilities, collectively ensuring stable and reliable power supply to the user end.
Power Generation Section Power generation is the starting point of the power system. Electricity production can be carried out through various forms such as hydroelectricity, thermal power, nuclear energy, wind energy, solar energy, etc. Power plants convert these natural resources into electric energy, transmitting it through high-voltage current to the transmission grid. Although this is the first stage to start working in the power system, it does not directly supply power to users.
Transmission Section The transmission grid transmits the electric energy generated by the power station to different regions at high voltage. Since energy loss occurs during current transmission, high voltage and low current must be used to reduce losses. The transmission grid, through multiple substations and lines, transmits electric energy from distant power plants to the distribution network closer to the users.
Distribution Section Distribution is an important part of the power system and the link closest to the users. The distribution network is responsible for converting the electric energy from the high-voltage grid, through substations, to medium and low voltage, and finally distributing the electric energy to various users, including residents, enterprises, and other users.
Composition and Function of the Distribution System
The distribution system is an important link in the power system, responsible for distributing the power that has been stepped down after passing through the substation to each user. According to different voltage levels, the distribution system is usually divided into high-voltage, medium-voltage, and low-voltage distribution systems.
High-Voltage Distribution System The high-voltage distribution system generally refers to the distribution network with a voltage level of 10kV to 35kV. This system mainly reduces the voltage of the electric energy from the transmission grid through substations and supplies power to large-scale industrial or commercial users. The role of the high-voltage distribution system is not only to distribute electric energy but also to ensure the stability and safety of power supply through certain control and protection systems.
Medium-Voltage Distribution System The voltage level of the medium-voltage distribution system is usually between 380V and 10kV. This part mainly distributes electric energy from the high-voltage distribution network to small enterprises, residential areas, etc. The medium-voltage distribution network not only undertakes the task of transmitting electric energy but also bears part of the load regulation function. In many cities, the medium-voltage distribution network is a key link in supporting regional power stability.
Low-Voltage Distribution System The voltage level of the low-voltage distribution system is 220V or 380V, mainly facing resident users and some small commercial users. The low-voltage distribution system is the part of the power system closest to the users, directly determining whether the last kilometer of power can smoothly reach every household and enterprise. Therefore, the stability and reliability of the low-voltage distribution network are crucial for power supply.
Secondary System in the Distribution System
The secondary system in the distribution system refers to equipment and systems used for automatic control, power dispatching, monitoring, and protection. The secondary system ensures reliable power supply through intelligent devices and technologies by monitoring, analyzing, and scheduling the power network in real-time.
Distribution Automation System Distribution automation is a major trend in the development of the power system. Through smart terminals, sensors, automated switches, and other equipment, the distribution automation system can monitor the state of the power grid in real-time, automatically regulate the flow of electricity, and quickly locate, isolate, and restore power supply in case of faults. Distribution automation not only improves the operational efficiency of the grid but also enhances the interference resistance of the power system.
Power Monitoring System The power monitoring system is mainly used to monitor the real-time status of the distribution network, obtain the operating data of power equipment, and provide decision support through data analysis. Modern power monitoring systems, through cloud computing, big data analysis, and other technical means, can precisely control and optimize each link of the distribution network.
Protection and Control System The role of the protection and control system in the power system cannot be ignored. Its main task is to ensure that when the distribution system encounters abnormalities, it can detect faults in time and quickly cut off the faulty circuit to prevent further damage to the system or cause accidents. The protection and control system can respond quickly through automated equipment, thus ensuring the safety of the power system.
Development Trends of the Distribution System
With the continuous increase in social demand for electricity, the development of the distribution system is facing unprecedented challenges. To solve various problems in power supply, the distribution system is moving towards intelligence, automation, and greenification.
Construction of Smart Grids The smart grid is the core component of the future power system. By integrating advanced information technology, automation technology, and new energy technology, the smart grid enables the distribution system to monitor, schedule, and optimize power distribution in real-time. With the support of the smart grid, the power system can better cope with issues such as the large-scale access of renewable energy and load fluctuations, achieving more efficient and green power supply.
Access of Distributed Energy With the rapid development of renewable energy, more and more distributed energy (such as solar and wind energy) is being connected to the distribution system. These distributed energy sources have fluctuating and uncertain power generation, posing a certain challenge to the stability of the distribution network. In the future, the distribution system needs to be more flexible and intelligently scheduled to deal with this variable power supply model.
Application of Energy Storage Technology The development of energy storage technology, especially battery energy storage technology, brings new opportunities to the distribution system. Through energy storage equipment, the distribution system can store excess electricity during peak supply times and release it during peak demand times, thereby balancing the grid load and improving the stability of the system.
Challenges Faced by the Distribution System
Although the distribution system is continuously progressing, it still faces many challenges in actual operation. For example, aging problems, equipment maintenance issues, and the access of renewable energy all bring pressure on the stable supply of electricity. Ensuring that the distribution network can maintain efficient operation even under large-scale load fluctuations and equipment failures is a pressing issue that the power industry needs to address. As intelligent and automated technologies continue to develop, the functions and efficiency of the distribution system will be greatly enhanced, and the future distribution system will be smarter, more reliable, and more efficient, providing strong support for sustainable development.